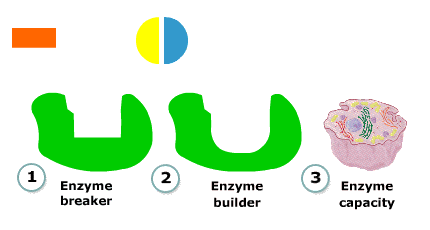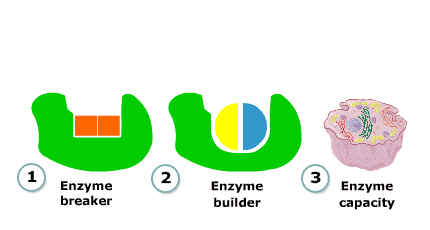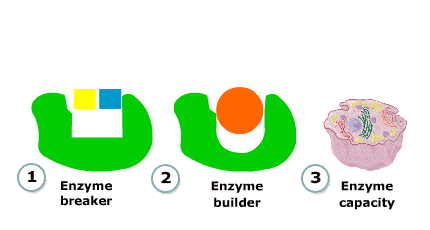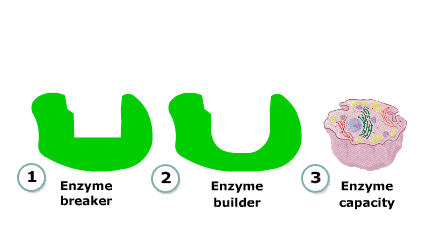
Enzyme breaker
Here, a substrate molecule binds at the active site.
The enzyme then helps to break it down into two smaller molecules, which then separate from the enzyme.
Another substrate molecule can then bind with the active site, and the process repeats.
Enzyme builder
Here, two substrate molecules bind at the enzyme's active site.
The enzyme then helps the two molecules combine to form one, larger molecule, which then separates from the enzyme. Two more substrate molecules can then bind with the active site, and the process repeats.
Enzyme capacity
One enzyme molecule can transform a huge number of substrate molecules in a very short time.
For example, one catalase molecule, in a liver cell, can change up to 6,000,000 substrate molecules every second. So cells only need relatively small amounts of enzymes to function.